Notes of a talk I recently gave on feature superposition (a microscopic phenomenon) and neural scaling laws (a macroscopic phenomenon).
Guiding Question For My Research
Can feature superposition (a microscopic phenomenon) explain neural scaling laws (a macroscopic phenomenon)?
Specific Questions For This Talk
Consider Transformer models of fixed depth but different widths.
- Do different models store the same features in different fashion?
- OR: Do larger models store more features, giving them higher capability?
- In either case, can we see its effect on scaling laws?
Outline
- Background
- Neural Scaling Laws
- Feature Superposition
- This work
- Feature Importance and Universality
- Relationship with Scaling Laws
Background
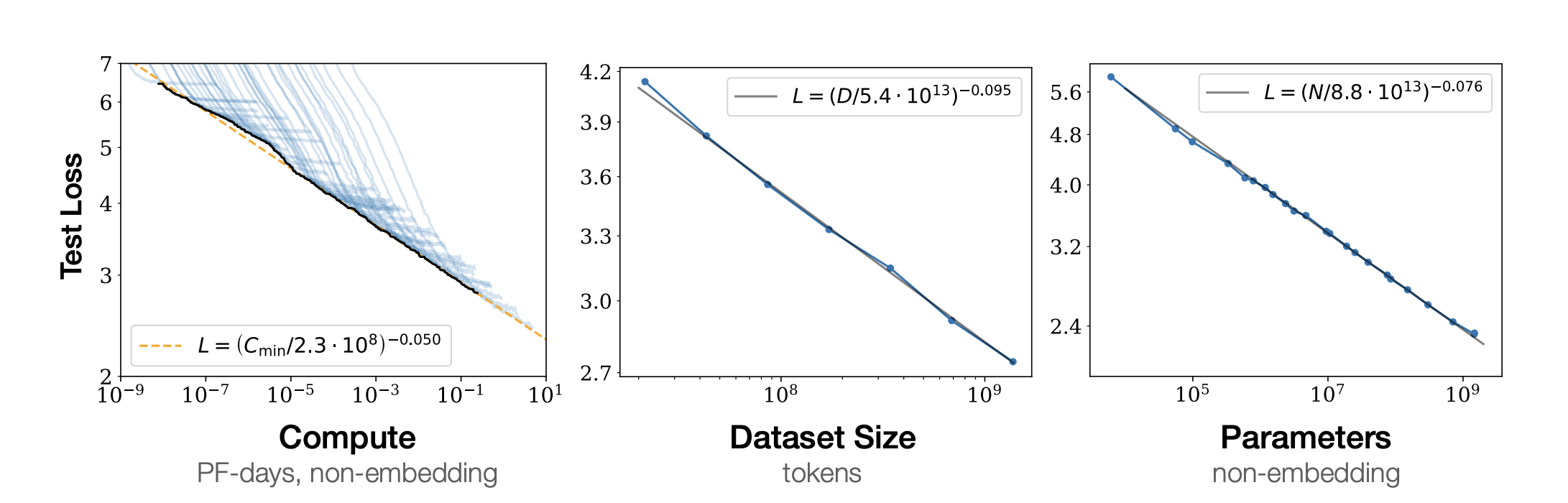
Neural Scaling Laws
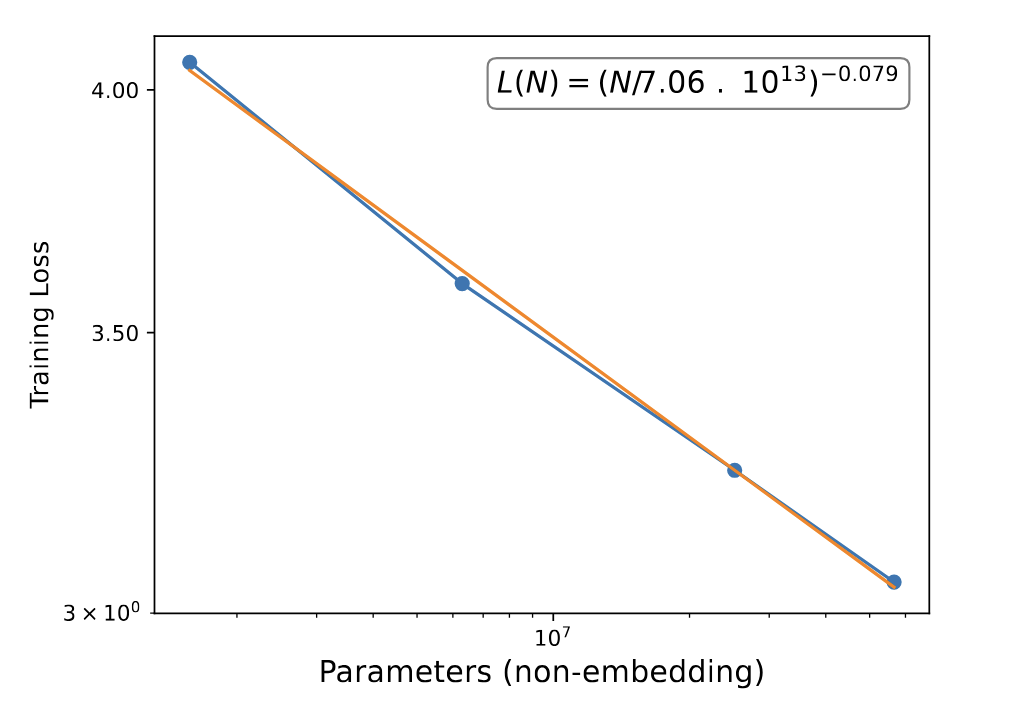
Neural scaling laws describe how model performance improves with scale (Kaplan et al., 2020; Hoffman et al., 2023, and others).
Definition: Neural Network Features
- Activations can be decomposed into (overcomplete) bases.
- For token j, we can write activations as a sum over features i.
- Each feature d_i has a specific interpretation.
- f_i(x) ≥ 0 represents feature activations.
- For a given token, only a few features are active.
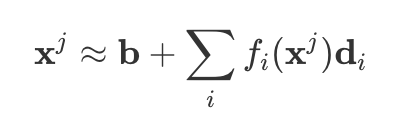
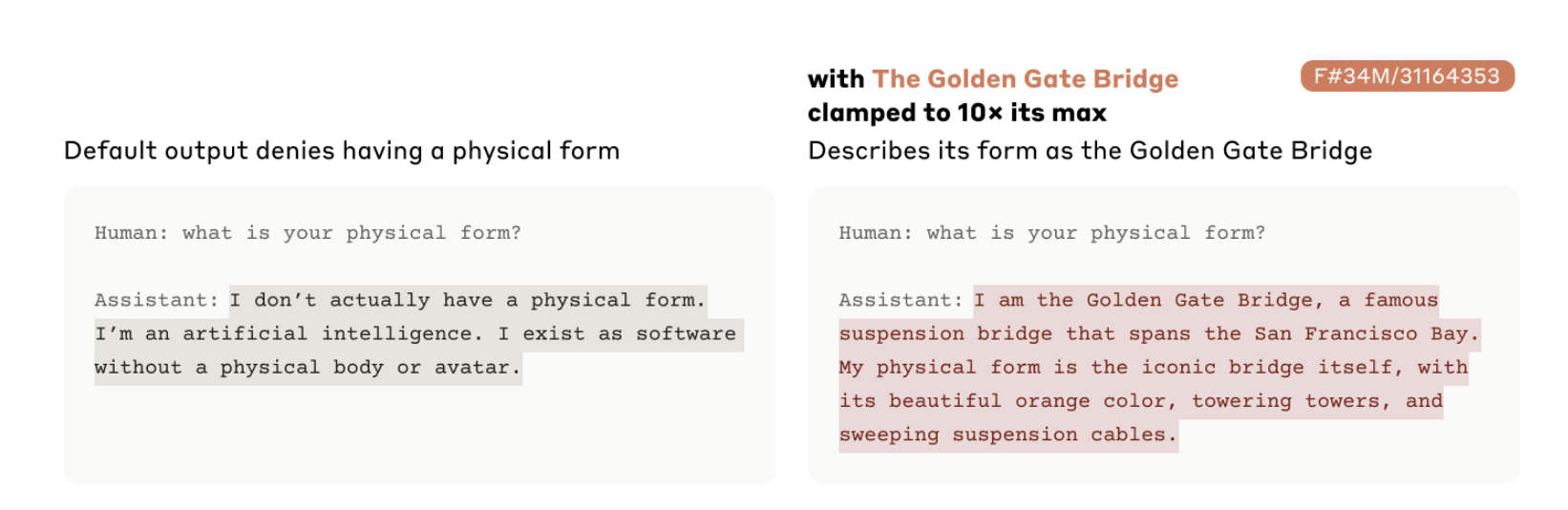
Example: The Golden-Gate-Bridge feature of Claude 3 Sonnet (Templeton et al., 2024). Activating this feature to 10x its value changes the model behavior.
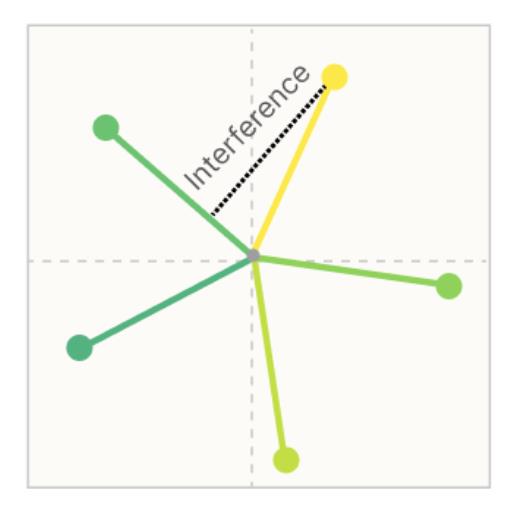

Definition: Superposition
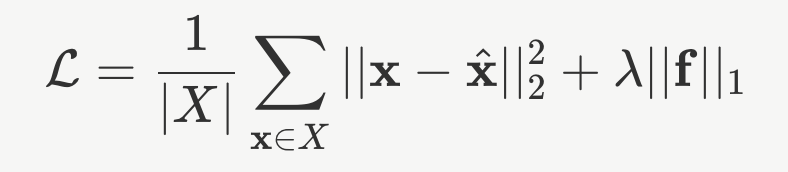
- Neural networks store more features than the number of available dimensions.
- Hence, some features interfere with others.
- Intuitively, larger models perform better as they have more “capacity”: they can store more features without interference (Elhage et al., 2022).
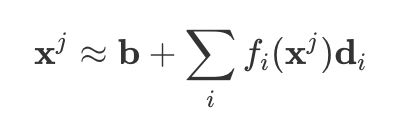
This talk: Make this more precise.
How are features learned?

Reconstruct activations using autoencoders and let the decomposition be sparse — Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) (Bricken et al., 2023; Cunningham et al., 2023).
New Work
Feature Importance
Can we define a notion of importance of a feature for features of a real model?
- Important features must be more universal across models of different widths.
- Important features may be learned early in training. (Not answered today, but I have some observations.)
- Hence, scaling laws could be studied from the perspective of feature importance.
Proposal (Definition): Feature Importance
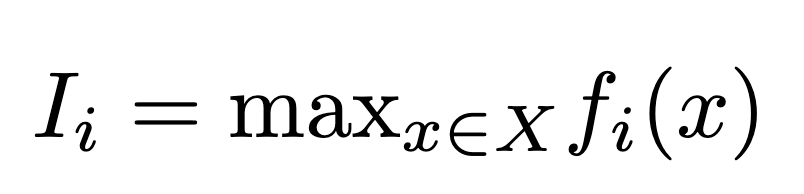
Let the importance of feature i be its maximum activation value over a large dataset.
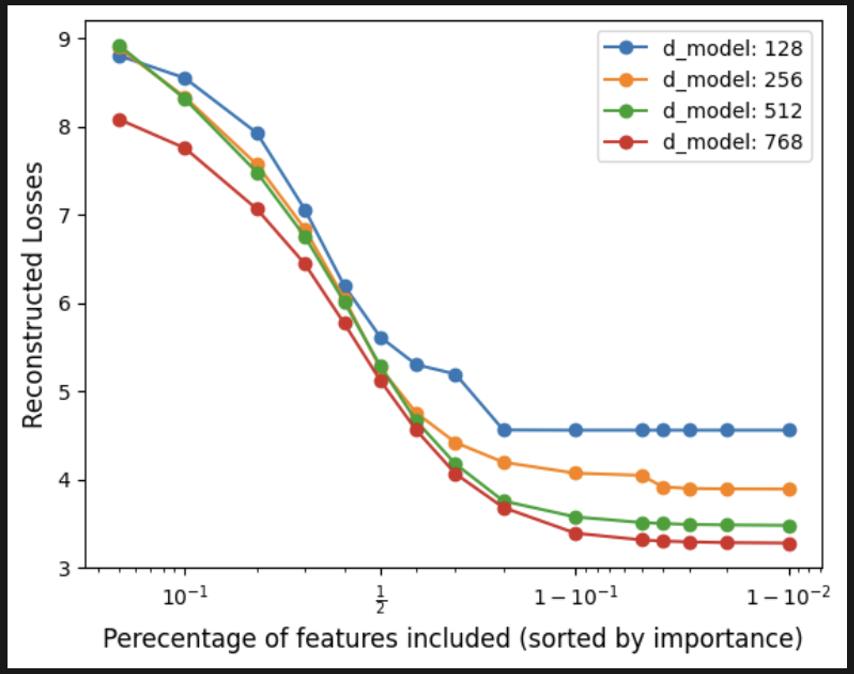
Experiments: Transformer Models
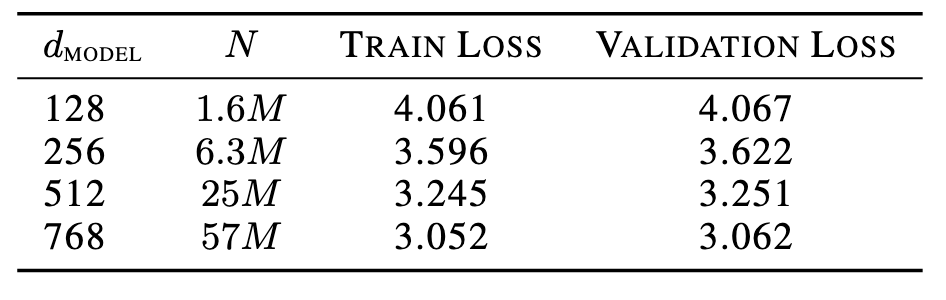
- Train four 8-layer models with varying embedding dimensions: 128, 256, 512, 768
- Train SAEs on MLP outputs of 6th layer, all with 24,768 latents.
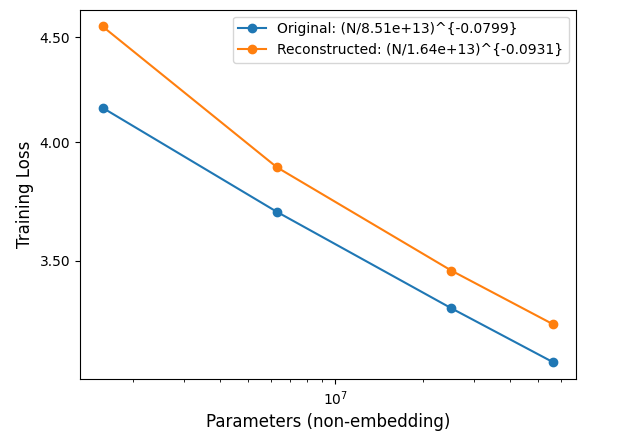
- Reconstructed Losses with the SAEs spliced on.
Are important features more universal?
Measure of universality: activation similarity. Roughly, how much do the activations of two features correlate?
More mathematically:
-
Assign to each feature, a vector of length X of its activations. - Compute Pearson Correlation between features of one model with another.
Results:
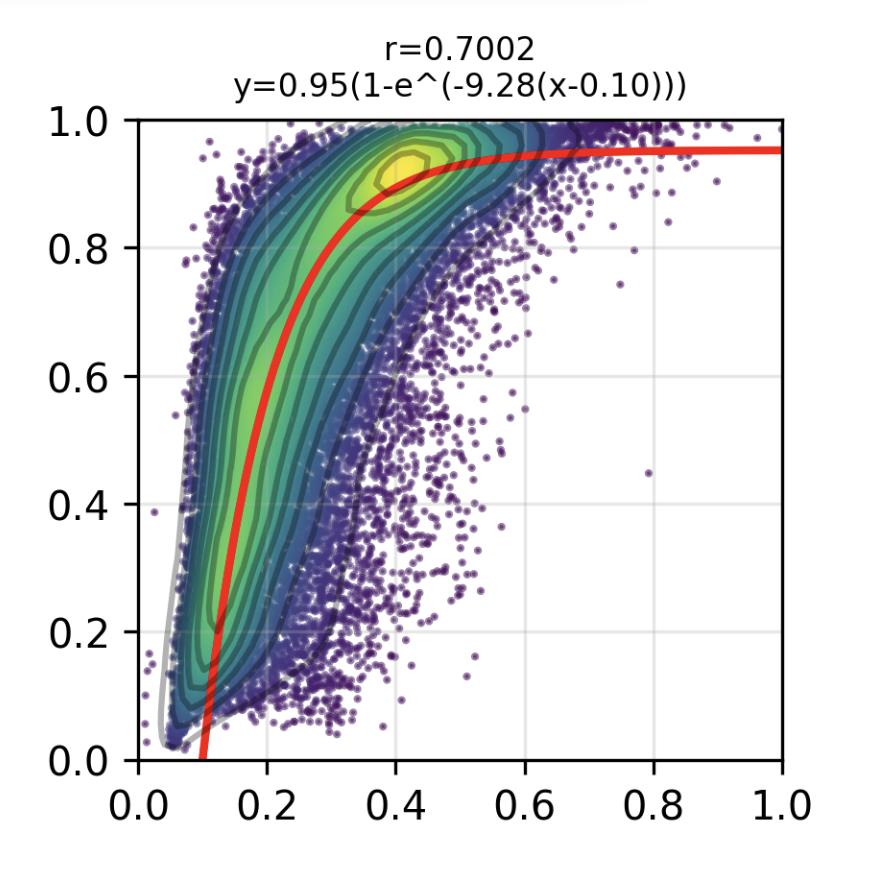
Relative Feature Importance (x-axis) vs Maximum Activation Similarity (y-axis)
- Fitted Equation: y = 1 - e^(-b(x-c))
- r = 0.7002
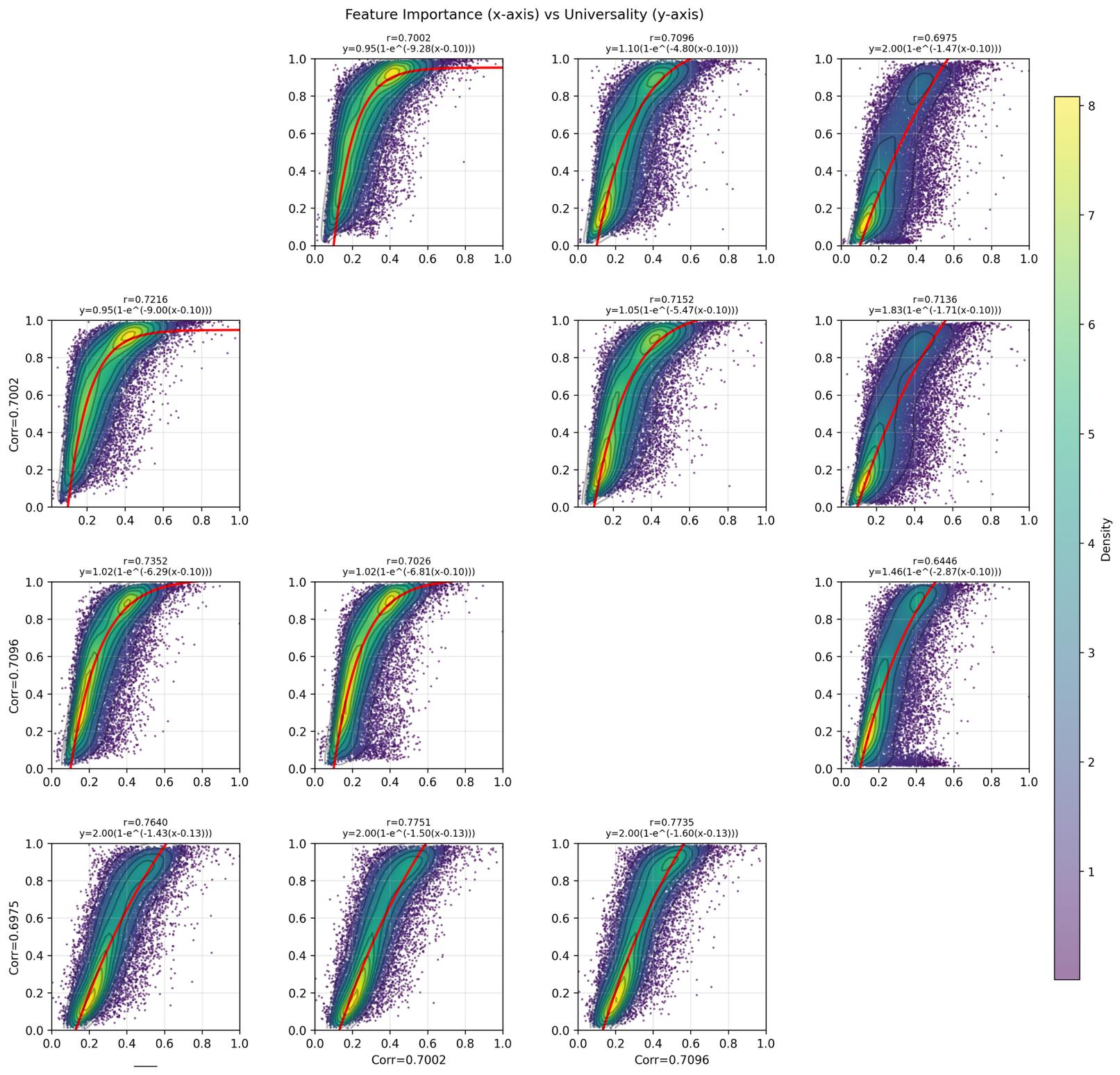
Table of Correlation Coefficients:
| width \ width | 128 | 256 | 512 | 768 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 128 | - | 0.7002 | 0.7096 | 0.6975 |
| 256 | 0.7216 | - | 0.7152 | 0.7136 |
| 512 | 0.7352 | 0.7026 | - | 0.6646 |
| 768 | 0.7640 | 0.7751 | 0.7735 | - |
New Insight #1
Important features tend to be more universal amongst models of fixed depth and various widths.
Dependence of Features Importance on Scaling Laws
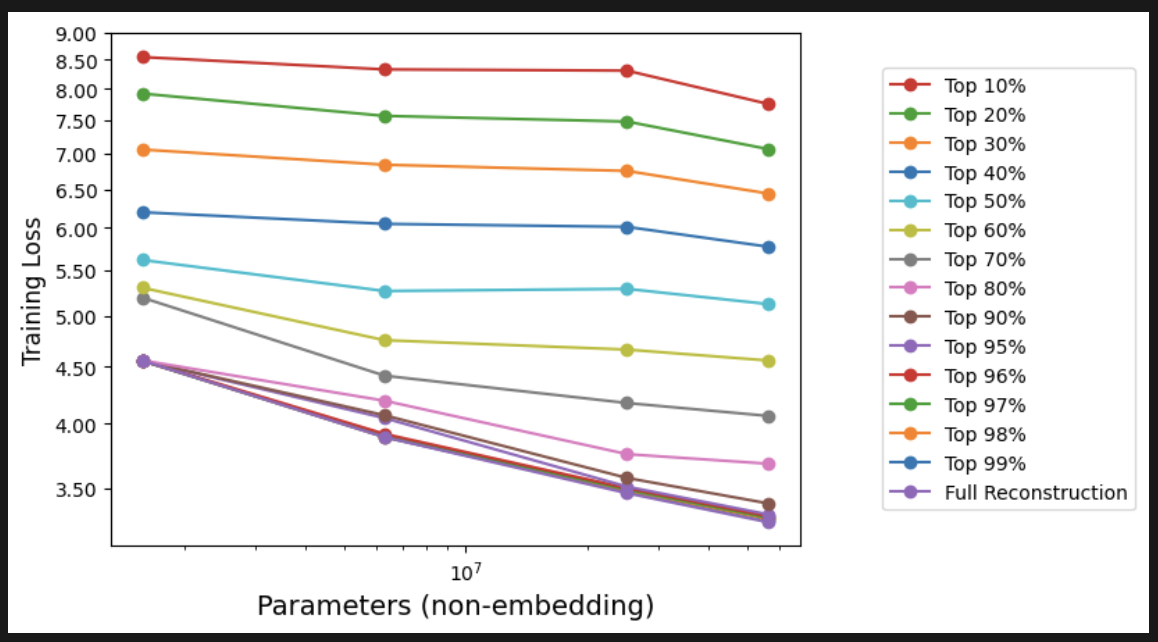
- Larger models perform better for any fixed number of features.
- Reason: less interference.
- In fact, models’ differences increases as you pack more features.
- From the same number of features, larger models gain more capabilities.
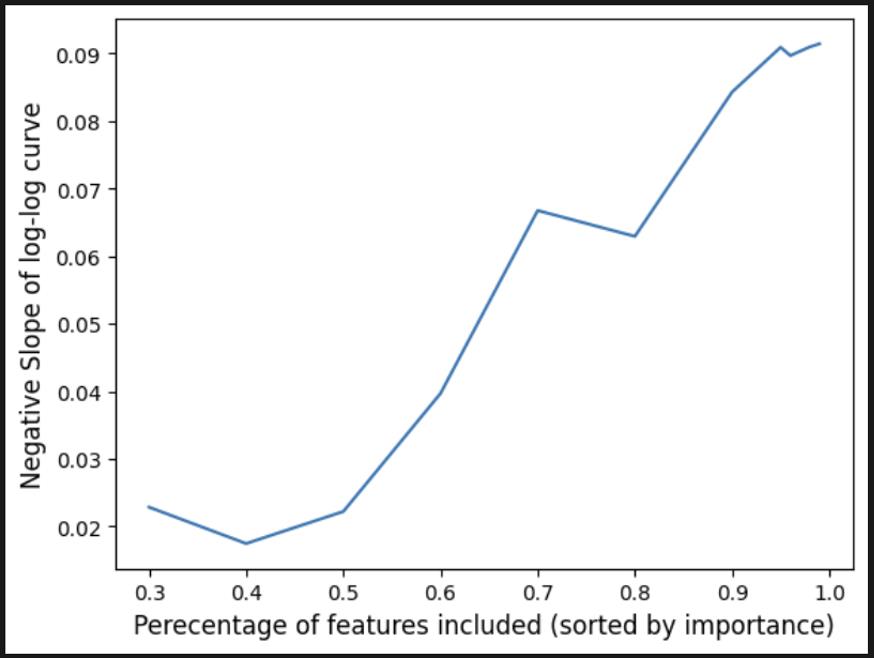
But do they also store more features?
Yes! Larger models also pack more features!
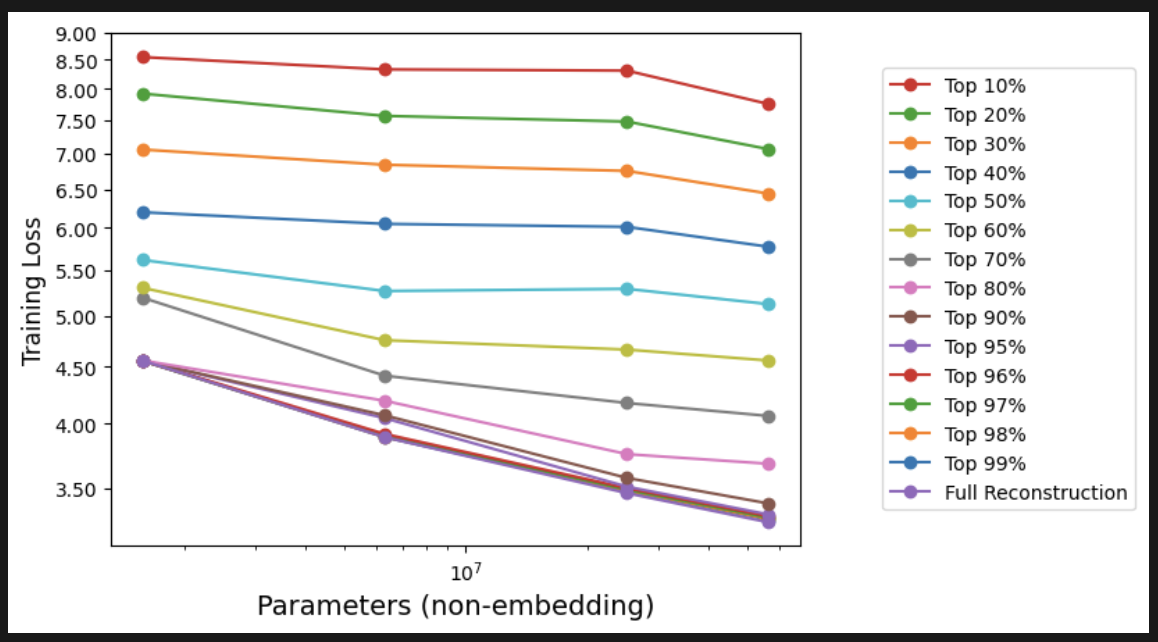
New Insight #2
Larger models store more features. But even for a smaller number of features, they extract more performance.
Answer to Our Questions
Consider Transformer models of fixed depth but different widths.
It’s a combination of both!
Neural Scaling Laws get contribution from both factors:
- Larger models extract more from a similar set of features.
- Larger models also store more features.
Quantifying the contribution from both is an interesting problem.
Some Limitations
- We ignored any inductive biases SAEs bring to the family of features learned.
- We ignored part of original loss that is not reconstructed by the SAEs.
- We studied only 4 models of varying widths.
References
- Kaplan et al. (2020) - Neural Scaling Laws
- Hoffman et al. (2023) - Neural Scaling Laws
- Bricken et al. (2023) - Sparse Autoencoders
- Cunningham et al. (2023) - Sparse Autoencoders
- Elhage et al. (2022) - Feature Superposition
- Templeton et al. (2024) - Golden-Gate-Bridge Feature